Frequency coverage is continuous from 1.8 to 30 megahertz.
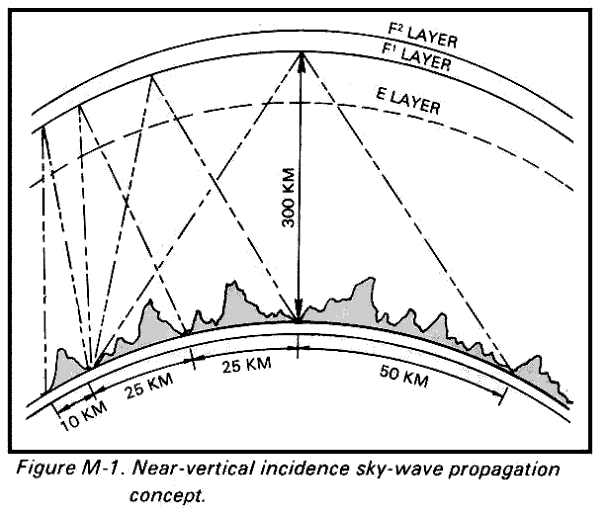
NVIS reflective function is optimized for sixty meters.
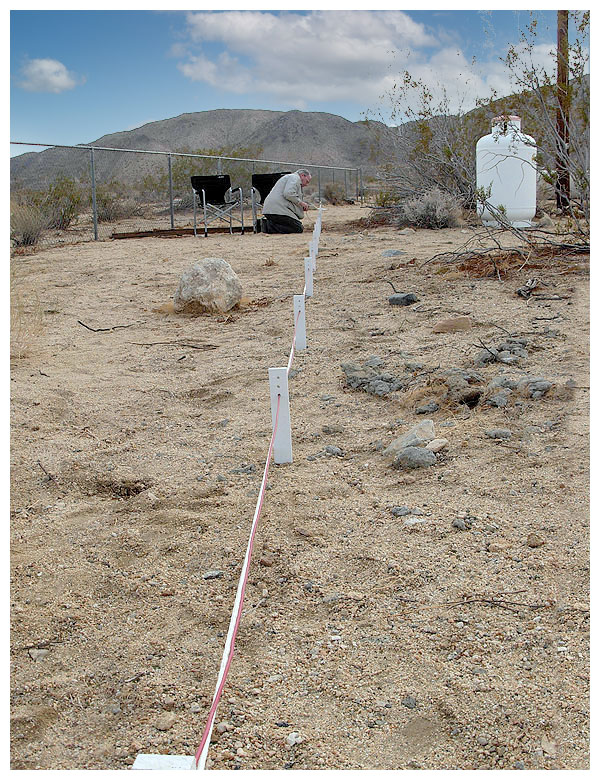
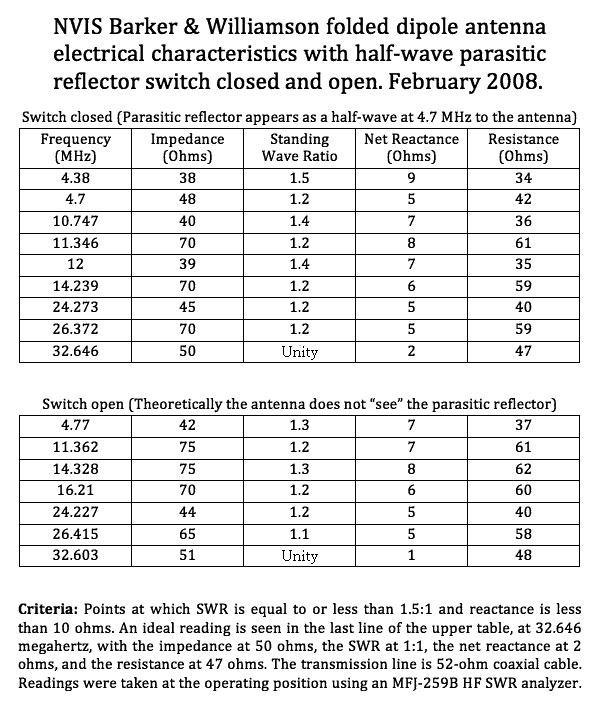

Installing the passive reflector prior to erecting the antenna.
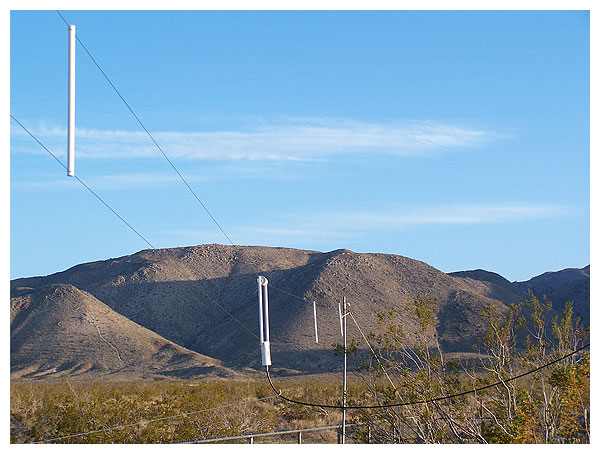

Looking south along the folded dipole antenna at AA6SC.
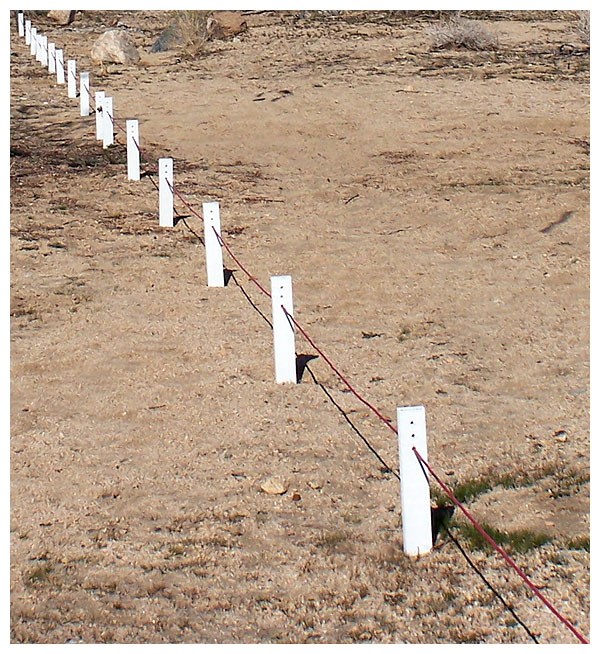

The 5-MHz parasitic reflector runs through wooden stakes.
The passive element is not grounded, nor wired to the dipole.

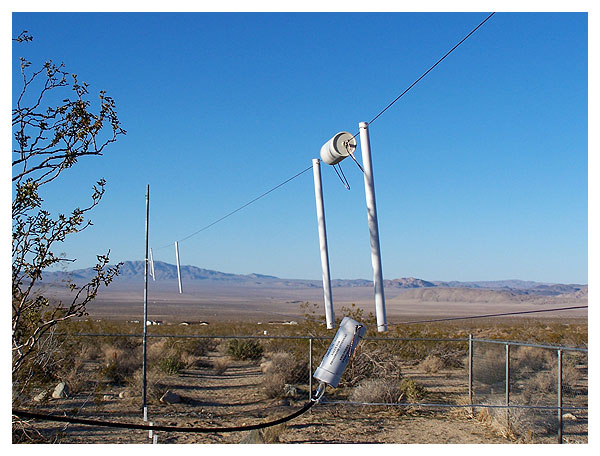
The reflector wire meets in the center at a toggle switch.
Opening the switch disrupts its tuned reflective properties.
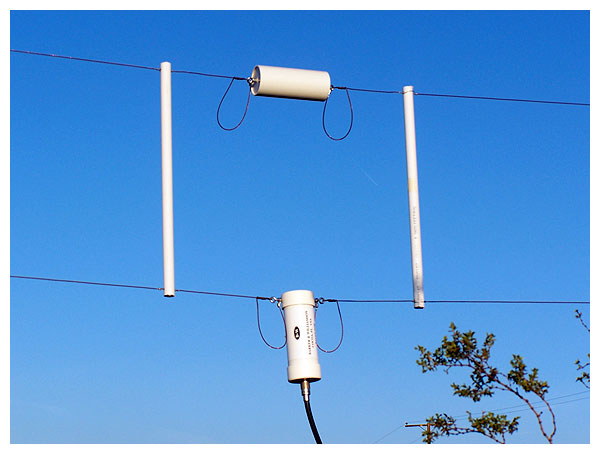
A close-up of the resistive termination and balun.

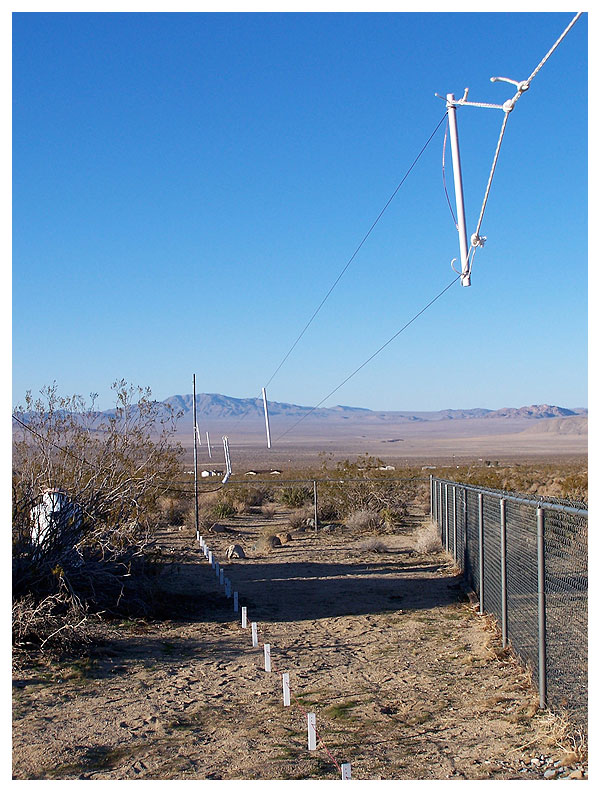
An alternate view of the feed point.
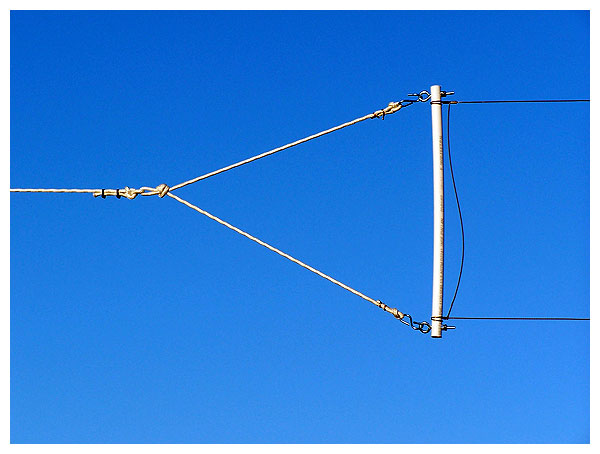
Detail view of the antenna’s northern end.
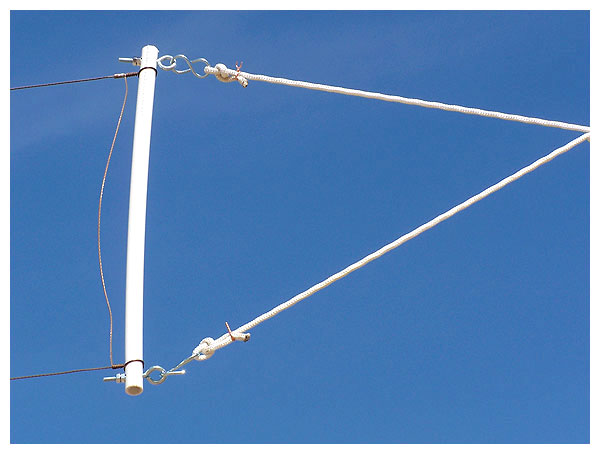
A close-up of the antenna’s southern end.

This folded dipole antenna is ninety feet in length.
Its reflector is ninety-six feet, four inches long
and is made of 12-gauge insulated copper wire.
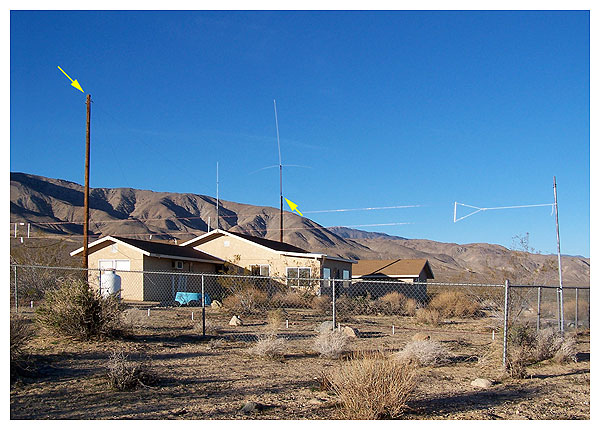

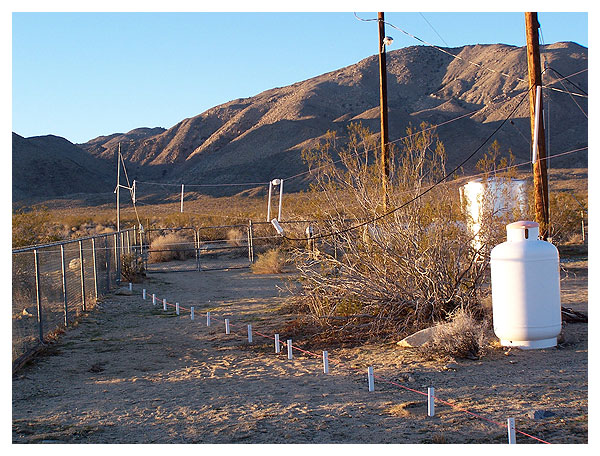
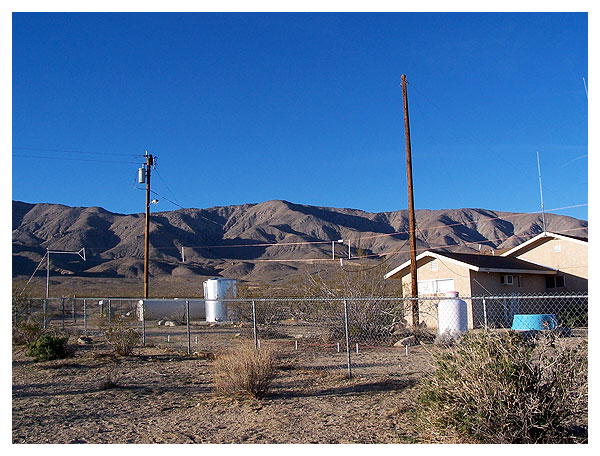
Other antennæ include two- and ten-meter ground planes,
and an HF long wire. The long wire stretches between
two utility poles shown marked with yellow arrows.
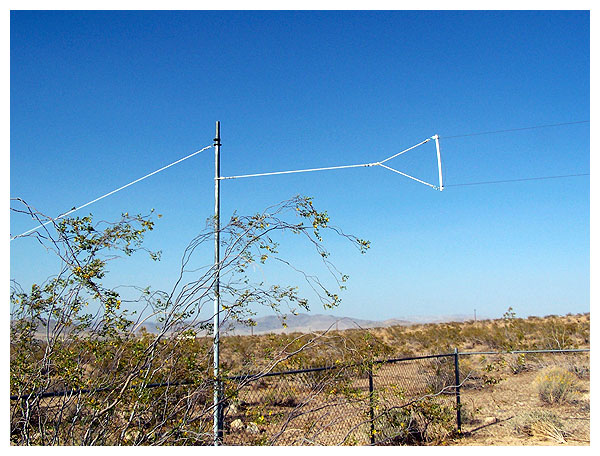

Masts are bolted to fence posts and guyed at their tops
to balance the stress of the antenna load.
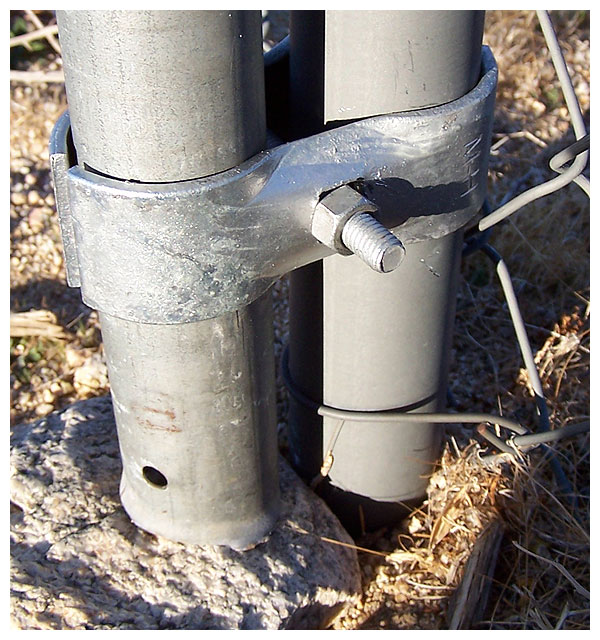

Two clamping techniques and two bolt types were
considered in order to combat desert winds.

Here we see ordinary galvanized nuts and bolts
used in a clamping configuration.
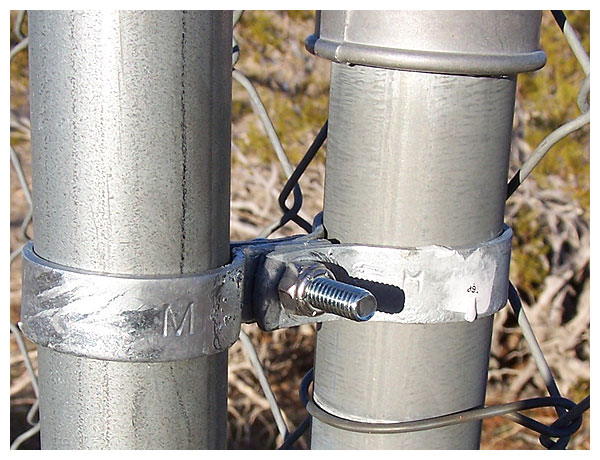

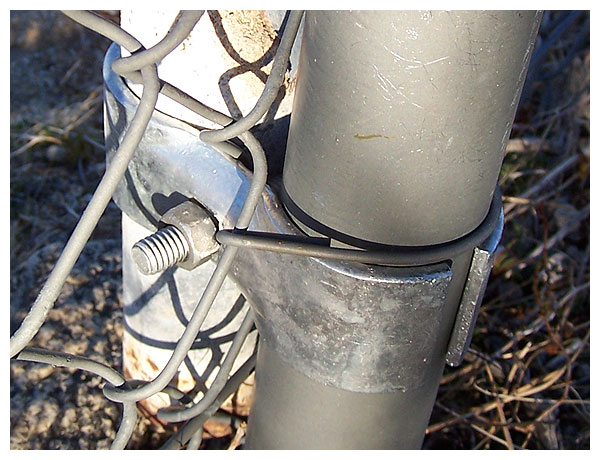
Plated bolts and nylon insert stop nuts hold separate
bands that independently surround each pipe.
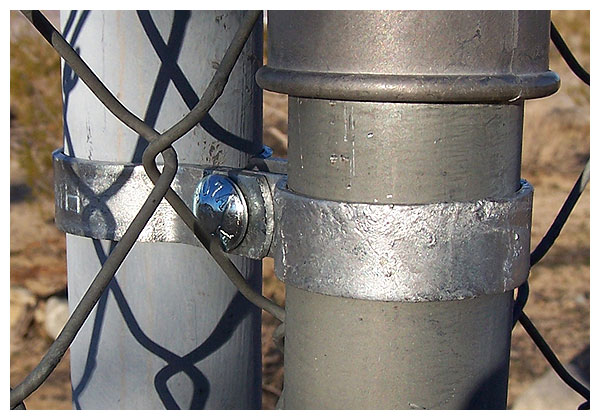

Two years later, both clamping methods remain secure.
Only the fence post bottom ends are buried in concrete.

The NVIS folded dipole and the long wire
are at right angles to each other.
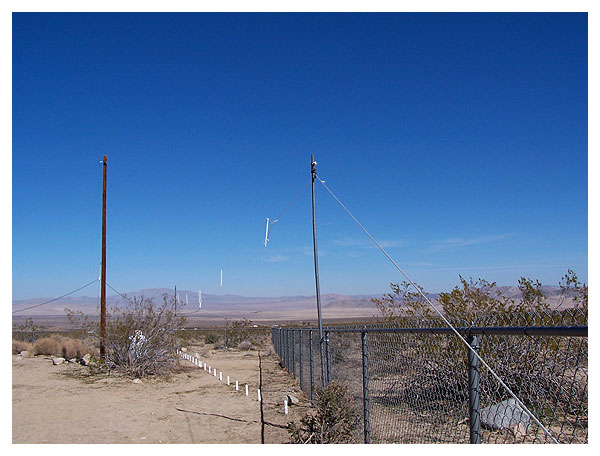

The upper lead of the dipole is 11 feet above the reflector.
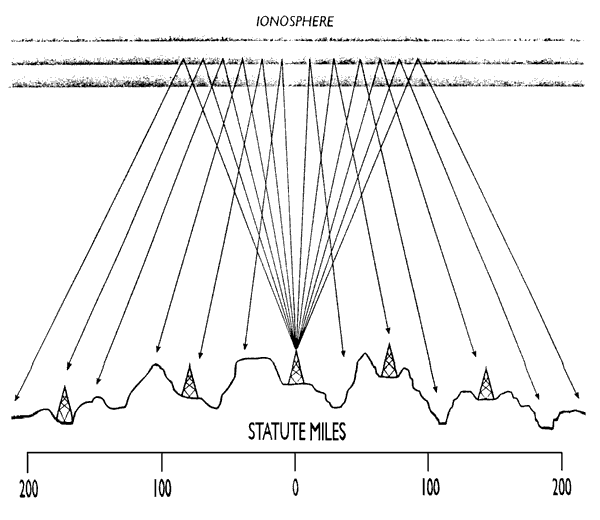
The objective of an NVIS array is to radiate most of the signal
straight up, where it will reflect off the ionosphere and return
to Earth with continuous coverage out to a 200-mile radius
or greater, but without a skip zone.
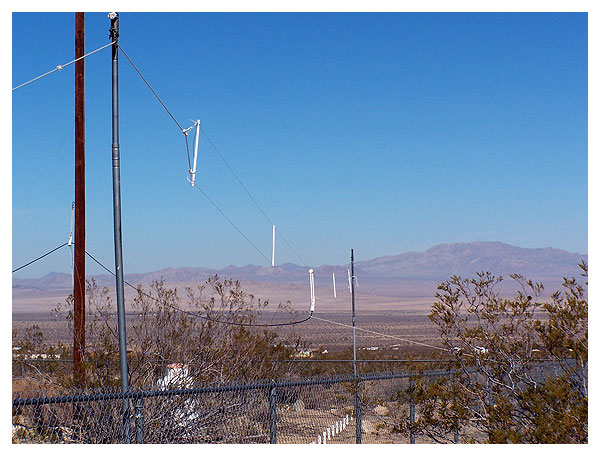

A white nylon line runs from the coaxial cable to the fence
to dampen the antenna’s swinging in the wind.

Observations: 1. Rapid fades are lessened when using the NVIS antenna compared to signals heard while using the long wire antenna. Sometimes the signal strength from Station A is greater than that from Station B while using the long wire, and switching to the NVIS dipole reverses this trend. As the two antennæ are at right angles to each other, with the long wire at more than twice the height above ground as the folded dipole, this comes as no surprise.
2. Atmospheric noise is less noticeable when using the NVIS antenna, particularly on forty meters. This may well be due to the fact that the NVIS array is at right angles to the Southern California Edison Company’s power line.
3. With an MFJ antenna analyzer connected to the NVIS coaxial transmission line at the operating position, opening and closing the parasitic reflector’s central switch causes slight variations in resistance, reactance, impedance, and VSWR readings.
4. Switching between the two hf antennæ often shows no appreciable change in received signal strength, while on some occasions it makes a huge difference of up to 6 dB. This too comes as no surprise.
5. It seems fair to say that any horizontal antenna could be configured for NVIS operation. These remarks are not meant to suggest that this folded dipole antenna was designed exclusively for NVIS applications. The 5-MHz parasitic reflector and the minimal height of the antenna are what make this installation suitable for NVIS use.
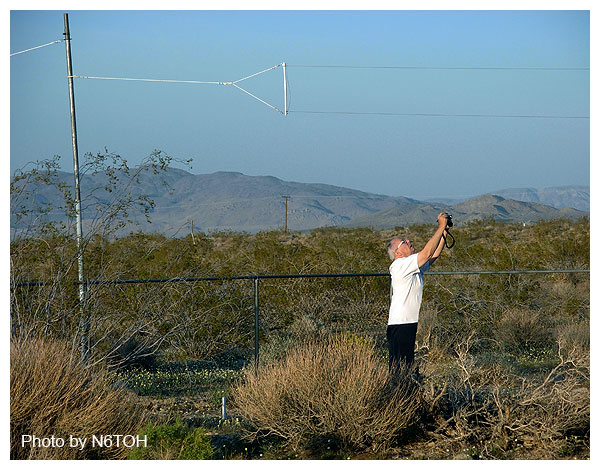

AA6SC attempts to find the best composition for photos on this page.
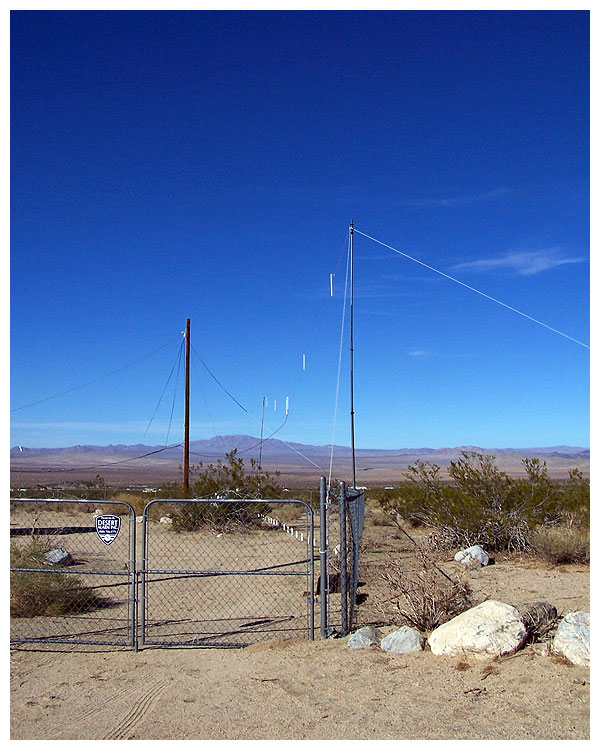

OCTOBER 2010 UPDATE: After two and a half years, I determined
that the antenna was not performing as well as I had hoped, so we
doubled its height to twenty-three feet.
